What is an Infection Control Audit?
An infection control audit is the process of proactively guarding healthcare facilities against the spread of diseases by identifying and setting controls for possible sources of infection. Also called infection control risk assessment, an infection control audit can help ensure patient safety and improve the quality of care.
What is an Infection Control Checklist?
An infection control checklist or infection control assessment tool is used in healthcare facilities such as hospitals, clinics, and nursing homes to assess cleanliness, infection control practices, and compliance with hygiene standards.
Infection control, through the effective use of infection control audit tools, can help prevent the spread of diseases amongst patients and staff and ensure the safety of healthcare facilities.
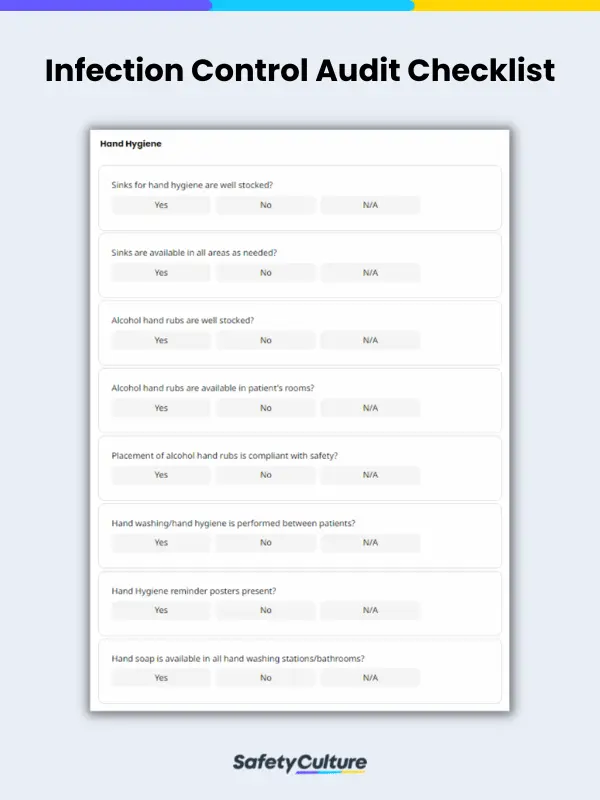
What Should an Infection Control Checklist Include?
An infection control checklist should include a regular review and inspection of the following items:
- Employee name
- Hand hygiene
- Clean utility
- Central supply/storage
- Patient rooms
- Patient kitchen/breakroom
- Employee kitchen/breakroom
- General unit
- Nurses station
- Medication room
- Isolation rooms
- Employee’s general knowledge of infection control
- Dirty utility room
- Patient shower room
How often should an infection control audit be completed?
The frequency of an infection control audit depends on the needs, current situation, and context of the healthcare institution. Generally, the International Federation of Infection Control (IFIC) affirms that an infection control audit should take place over a defined time using a rapid audit cycle plan or an overall annual plan.
For example, each specific area of an organization such as hand hygiene, indwelling lines, and urinary catheters, should be audited one day at a time and in an alternating pattern. Having audited each area twice with a 2-day interval, the infection control team will have results about the effectiveness of their safety measures within a week.
To provide a clearer picture of a sample infection control audit schedule, refer to the table below:
| Day 1 | Day 2 | Day 3 | Day 4 | Day 5 | Day 6 | Day 7 | |
| Hand Hygiene | Analyze data, communicate results, and apply improvement measures | ||||||
| Indwelling Lines | |||||||
| Urinary Catheters |
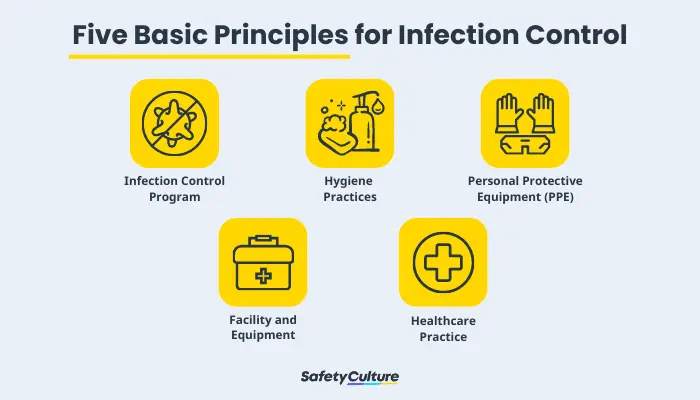
What are the five basic principles for infection control?
Infection control audits cover all possible sources of infection in healthcare facilities with particular focus on the following (source: CDC):
- Infection control program
The healthcare facility should have written infection control policies and procedures. Healthcare staff, as well as patients and their caregivers, should be empowered with training and knowledge on infection control.
Special circumstances also call for strict compliance with measures implemented to prevent fast-spreading diseases from taking place in healthcare facilities. - Hygiene practices
Competency on proper hand hygiene is a must, particularly for healthcare providers. Routine monitoring of hand hygiene practices through internal audits can help ensure that proper hand hygiene is being practiced.
- Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
One way to protect healthcare professionals from infection is through the proper use of PPE, which is standard procedure in any job that involves health risks.
- Facility and equipment
Healthcare professionals should be knowledgeable in the use of ventilators and other hospital equipment. The proper disinfection of tools and equipment and the cleanliness of the healthcare facility must be maintained at all times.
- Healthcare practice
Proper insertion and maintenance of catheters, injection practices, and other medical services must be done in adherence to the infection control protocols of the facility.