What is PDCA?
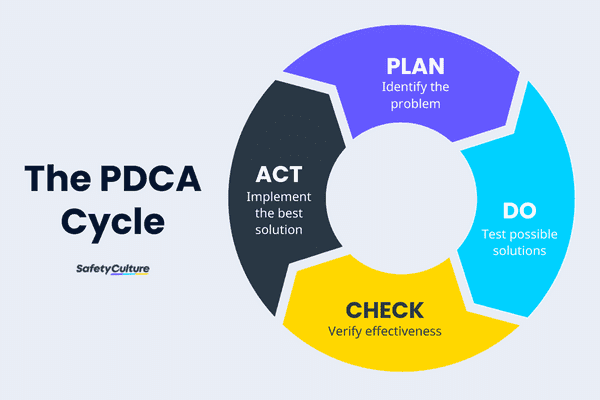
The PDCA or Plan-Do-Check-Act is a four-step cyclical method used to streamline business processes and continuously improve product and service quality. Through a continuous application, PDCA cycle aims to observe how processes work, recognize rooms for improvement, identify which methods work best in addressing problems, and verify the effectiveness of implemented solutions.
The PDCA Cycle
The PDCA Cycle
The PDCA method is used when teams are developing any new products, starting a new project, implementing any change, or when continuous improvement is generally sought. It is also utilized to avoid repeating previous mistakes and errors in operations.
The step-by-step approach of PDCA also offers time-saving opportunities by proactively catching ineffective solutions before implementing them on a larger scale. Furthermore, the PDCA cycle is versatile and can be applied across multiple industries and various sectors.
Stages of PDCA
The stages of the PDCA cycle consist of four steps and are implemented repeatedly for Continuous Process Improvement (CPI). It can be modified based on the result of each cycle and maximized to its full potential with each use. Let’s look at each step individually.
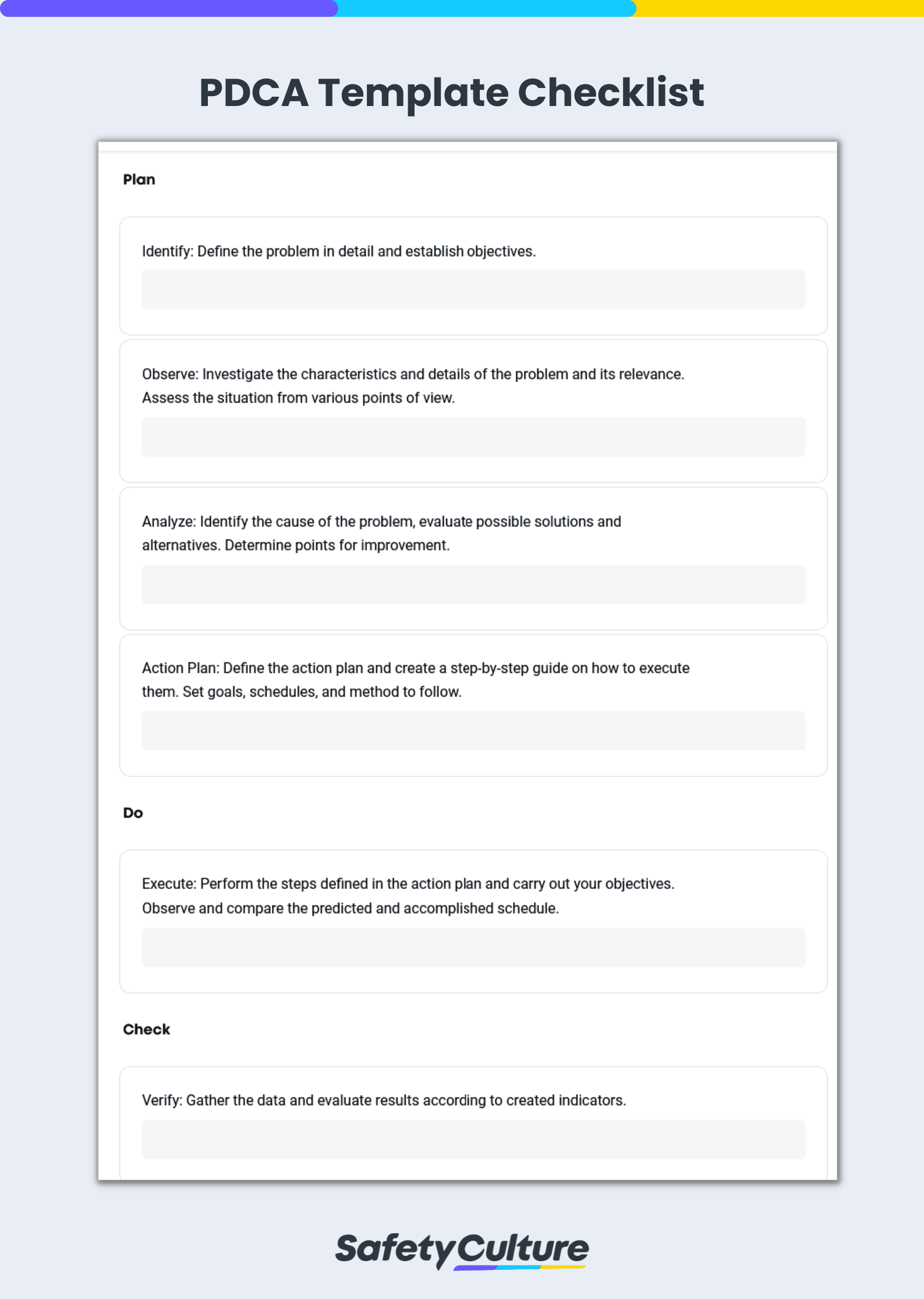
Plan
This initial stage identifies the problem, spots inefficiencies in the process, and establishes the goals and objectives of the plan. It contains existing data such as standard, methods, and procedures currently used.
It should also clearly state the schedule to follow and present possible solutions to the problems identified, or alternatives to improve the current process. The completion of this stage should feature the main framework or the action plan to perform, including the steps and the individuals involved.
Do
This is the execution stage—perform the steps defined on the first part and test possible solutions—but on a smaller scale. The goal at this stage is to recognize which of the alternatives work best for the project before fully implementing it.
Observe the accomplished results and compare them with the predicted outcome according to the action plan.
Check
This stage evaluates the initial test done with the goal of identifying its effectiveness. Monitor the result using the measures indicated and assess if there’s room for improvement or if it works according to its purpose.
If adjustments are needed, go back to the first stage—Plan—and repeat until a comprehensive solution is reached. If it’s considered a success, proceed to the next step.
Act
On a larger scale, this stage implements the best solution identified to tackle the problem initially identified. Document and measure the results obtained, and validate the problem-solving process for its effectiveness.
Note that the PDCA method is a cycle and it is best used incrementally if a continuous improvement is sought. Use the action plan as a standardized baseline, evaluate if there are further opportunities for improvement, and modify after each cycle to make it even more efficient.
How Does it Improve Your Business
Similar to the approach of the Japanese business philosophy Kaizen, the PDCA cycle aims for continuous improvement. It is used by organizations to enhance current processes and execute operations efficiently. Below are three common business processes that use the PDCA approach to improve performance:
- Health and Safety – PDCA method is commonly used to describe occupational health and safety management in both the HSG65 and ISO 45001 standards. Organizations use this approach to have a clear understanding of the goals, easily quantify the results based on the indicators provided, and improve processes by spotting inefficiencies in the health and safety systems and adjusting them accordingly.
- Quality Management– One of the widely used methods of monitoring quality assurance as well as complying with quality management system or the ISO 9001, is through the PDCA system. It analyzes existing procedures and methods, builds hypotheses through the gathered data, and executes tests continuously to spot any issues or room for improvement in the process. Through this method, organizations can work to continuously improve products and avoid recurring mistakes.
- Compliance with Industry Standards – The PDCA approach is also performed to streamline conformance to industry standards and other industry regulations. This eases the monitoring process and helps in successfully determining opportunities to operate efficiently.
What is a PDCA Template?
A PDCA template is a tool that organizations use in implementing the PDCA business approach. It serves as a guide in executing a plan and carrying out the changes initially identified.
According to the set goals and objectives, templates offer a comprehensive overview of the plan from start to finish, and help in spotting inefficiencies that need to be addressed.
The various templates used for this approach depend on the industry and specific needs of the business. Through a comprehensive PDCA Template, companies can easily monitor the progress of the plan and proactively execute any changes needed to improve business performance.
PDCA Example
To provide you with a clearer picture of how PDCA can be used to improve your operations, here’s an example:
Scenario: Let’s say you work as a manager at a manufacturing company, and you’ve noticed that the production process for a particular product is inefficient, leading to high defect rates and increased costs.
1. Plan
- Identify the problem: In this case, the problem is the inefficiency in the production process, leading to high defect rates and increased costs.
- Set objectives: Set specific objectives for improvement, such as reducing defect rates by 20% and decreasing production costs by 15% within the next quarter.
- Develop a plan: Create a detailed plan that outlines the steps to achieve these objectives. This might involve analyzing the current process, identifying bottlenecks, and researching best practices in manufacturing.
2. Do
- Implement the plan: Put the plan into action by making changes to the production process. This could include reorganizing workstations, implementing new equipment, and providing additional training to employees.
- Document changes: Document all the changes made during this phase so that you can measure their effectiveness later.
3. Check
- Monitor progress: Track and monitor the production process after implementing the changes. Collect data on defect rates and production costs to assess whether you’re moving towards your objectives.
- Compare results: Compare the current data with the baseline data from before the changes were implemented. This will help you determine if the changes are having a positive impact.
4. Act
- Analyze results: Based on the data and feedback collected, analyze the results of the changes. Are defect rates decreasing? Are production costs going down as expected?
- Make adjustments: If the results are not meeting your objectives, it’s time to make adjustments. This could involve fine-tuning the production process, providing additional training, or exploring other solutions.
- Standardize and document: Once you’ve achieved your objectives, standardize the improved process and document it thoroughly. This will ensure that the improvements are sustained over time.
Further, click these links if you want to see a PDCA example in the format of a PDF or digital report.
FAQs about PDCA Templates
When writing a PDCA report, make sure to include all the basic information of the project, as well as the data you’ve collected throughout the PDCA cycle. With this report, also document the following:
- Title and introduction – project name and other essential information
- Plan – details about the problem, observations, and other analyzations
- Do – actions you did to address the problem
- Check – data regarding the result of the first two steps and confirm if the plan worked
- Act – specific actions for improvement based on findings
- Conclusion– summary of the key takeaways from the PDCA cycle
- Recommendations – Actions for further improvement beyond the current cycle
- Completion – necessary signatures
PDCA is a problem-solving and continuous improvement methodology used in various quality management approaches, including both Lean and Six Sigma. It is not exclusive to either Lean or Six Sigma but is commonly employed in both methodologies.
PDCA is a general problem-solving and continuous improvement methodology that can be applied broadly to various processes and situations. On the other hand, DMAIC or Define-Measure-Analyze-Improve-Control is a specific methodology within the Six Sigma framework, primarily used to improve processes with a focus on reducing defects and achieving a specific quality standard.