What is QFD?
Quality Function Deployment (QFD) is a proactive, focused approach used in taking the Voice of the Customer (VOC) into account and then carrying out effective responses to customer expectations and needs during the design and production stages. Initially considered a form of cause-and-effect analysis, QFD is an essential tool not just for quality management but also for planning.
Originally developed in Japan by Professors Yoji Akao and Shigeru Mizuno in the late 1960s while working for Mitsubishi’s shipyard, QFD was later adopted and widely used by other companies such as Toyota and its suppliers. Consequently, the methodology was introduced in the US during the late 1980s primarily by automotive companies and electronics manufacturers. It’s also commonly known as a basic Total Quality Management (TQM) tool, being used by organizations in the manufacturing and healthcare industries, among others.
What is the Importance of Quality Function Deployment?
The goal was to create a methodology that integrates customer satisfaction into a product before implementing its manufacturing process. This presents a more proactive approach than other methods of quality control that focus on fixing customer issues during or after manufacturing.
Usually, customer requirements are communicated in the form of qualitative terms such as “safe,” “user friendly,” “ergonomic,” and so on. For organizations to effectively develop a product or service, these qualitative terms from customers need to be translated into quantitative design requirements. This is where QFD comes in. By combining various matrices to form a comprehensive house-like structure called the “House of Quality”, manufacturers and production facilities can come up with a prioritized list of customer needs and pain points and a systematic process of integrating them into the design of the product or service.
Hence, organizations can then make better decisions after weighing customer requirements and considering how the products or services go against the competition in the market. How QFD helps in this aspect is that it provides the needed documentation for the overall decision-making process.
Benefits of QFD
Now, how does this approach help organizations ensure the quality of their processes, particularly in product development? To summarize, here are a few of the major advantages of using QFD:
- Gain a better understanding of your customers – Be able to predict, know, and act on what they need, either stated or unstated, and provide a better customer experience.
- Utilize customer feedback for continuous improvement – Transform what the customers need into quantifiable business goals through the form of performance metrics, process controls, and more.
- Establish a better structure of requirements – The various stages of product development require efforts across departments, and inefficiencies in the process may occur. QFD helps build a standardized system that minimizes unnecessary risks and bottlenecks.
- Have an efficient way of allocating resources – By knowing the priority list of the customer requirements to be implemented, organizations can then be more intentional and focus on critical improvement opportunities.
What is House of Quality?
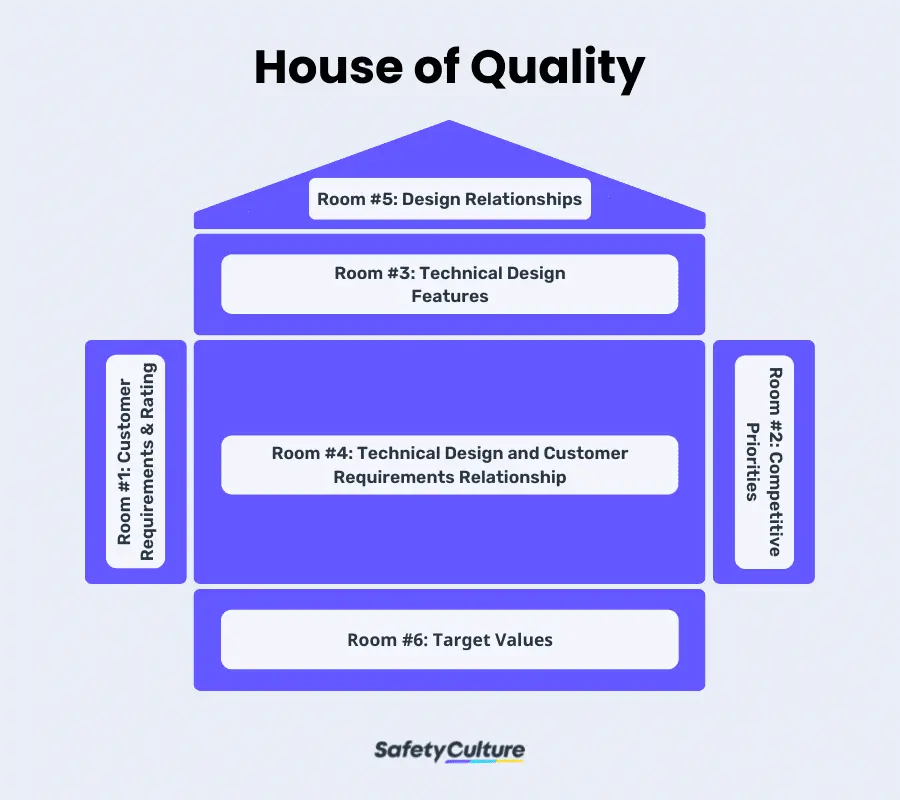
Also known as the product planning matrix, the House of Quality (HoQ) is practically the most essential stage of the QFD. This is where every bit of detail must be taken into consideration, as it’s going to set the pace for the succeeding stages of the four-phase QFD. Further, HoQ serves as a primary graphical representation of the product planning and development process.
House of Quality Example | QFD Matrix
In general, there are 6 main rooms or areas inside the House of Quality. Apart from answering the question “How do I fill out a QFD?,” these rooms also give an overview of how to effectively use the House of Quality template:
- Customer Requirements and Rating – Located at the left side of the house, this room lists the customer requirements gathered from the research and how they’re ranked based on their degree of importance (can use a scale of 1 to 5).
- Competitive Priorities – Placed on the right side of the house, this part outlines the top points of comparison between the customer requirements and the needed innovations based on competitor analysis.
- Technical Design Features – Listing the design features of the product, this section is placed just above the base, making it the attic of the house.
- Technical Design and Customer Requirements Relationships – Found at the base of the house below the attic, this part is responsible for visualizing and rating the impact of the design features on the priority list of customer requirements.
- Design Relationships – Also known as the roof matrix, this describes the interrelationship between the design features.
- Target Values – Lastly, the basement of the house lists the target values that serve as an organization’s way of quantifying objective measures to help evaluate each design feature or characteristic.
Digitize the way you Work
Empower your team with SafetyCulture to perform checks, train staff, report issues, and automate tasks with our digital platform.
Get Started for FreeWhat are the 4 Phases of QFD?
The 4 Phases of QFD
QFD enables cross-functional teams to collaborate and find a balance between customer needs and technical requirements. This is crucial in streamlining the way manufacturers and production facilities decide what kind of features or characteristics they should include in their products and services that customers will buy and value.
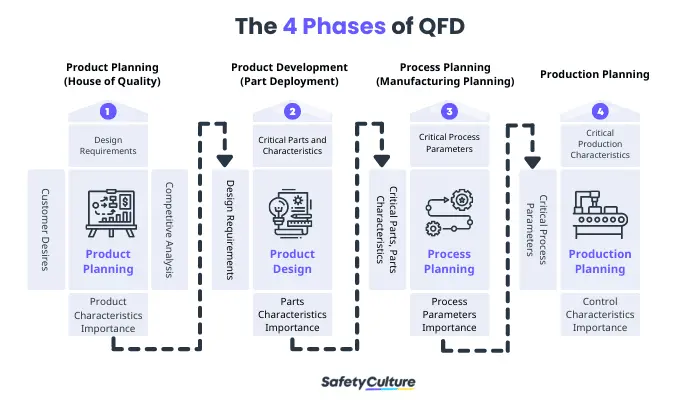
The comprehensive process of QFD is divided into 4 major phases: Product Planning, Product Development, Process Planning, and Production Planning. Each matrix or visual representation used under each of the 4 phases is related to the previous one. Let’s look into what happens under each stage.
1. Product Planning
In this stage, the House of Quality matrix is used to translate customer needs into design requirements. The Voice of the Customer (VOC) is gathered through conducting Focus Group Discussions (FGDs), interviews, and other similar methods using Voice of the Customer templates. Then, feedback and insights from such customer requirements are lined up for design and product features considerations.
As this phase will help set the pacing of the entire QFD process, it’s important to cover various aspects as well. These include identifying the underlying—apart from the obvious, stated ones—customer requirements, characteristics of possible market offerings, and competitive opportunities. It’s also crucial to note that this stage is typically led by the Marketing department.
2. Product Development
This phase enables the team to specify design requirements by identifying critical parts and assembly components. These are then based on the prioritized list of offering characteristics gathered in the Product Planning phase using the House of Quality matrix.
3. Process Planning
The third phase involves deciding on the design manufacturing and assembly process that best addresses the requirements discussed in the Product Development phase. Teams responsible for this aspect must be able to define the required operational guidelines, elements, and parameters.
4. Production Planning
The final phase is where process control methods are established, along with the production and inspection processes. These are key to ensuring that the characteristics are met and continuously undergo evaluation and improvement.
FAQs
As mentioned in the Importance section of this brief guide, QFD is a more proactive approach in such a way that it aims to incorporate customer feedback during the initial stages of production and manufacturing processes. Also, most quality initiatives focus on minimizing or eliminating errors—human or machine-made—to produce maximum results and achieve zero defects. Unlike other quality management tools, QFD takes the extra step to ensure that design processes capture customer requirements—underlying or stated—toward positive experiences and valuable offerings.
The overall methodology of Six Sigma lies on the principle of gathering and integrating the VOC throughout an organization’s quality process. QFD is an effective tool to do so, as the first and most essential stage involved in it requires obtaining customer requirements using the House of Quality or product planning matrix.
As the principle and practice of Total Quality Management (TQM) must be present in every aspect of the organization, QFD provides ways to seamlessly integrate its best practices into every stage of the product development process. One of the main principles of TQM is Customer Focus, in which the comprehensive methodology of QFD is most applicable with its core emphasizing customer requirements in the production process.




